Researchers have identified a new form of cyberattack termed “LLMjacking,” which exploits stolen cloud credentials to hijack cloud-hosted large language models (LLMs).
This sophisticated attack leads to substantial financial losses and poses significant risks to data security.
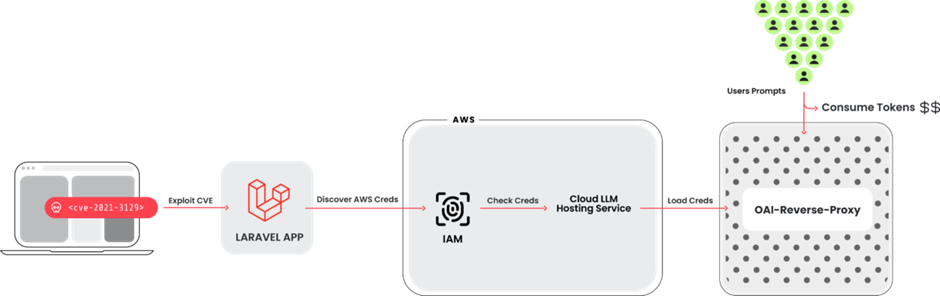
LLMjacking involves attackers gaining unauthorized access to cloud environments through compromised credentials, initially sourced from vulnerabilities in widely used frameworks like Laravel (CVE-2021-3129).
Once inside, the attackers target LLM services such as Anthropic’s Claude models, manipulating these resources to incur excessive costs and potentially extract sensitive training data.
If undetected, an LLMjacking attack can lead to daily costs upwards of $46,000, as attackers maximize the usage of LLM services to their financial benefit.
This burdens the legitimate account holders with hefty bills and can disrupt normal business operations by maxing out LLM quotas.
Beyond financial damage, there is a looming threat of intellectual property theft.
Attackers could potentially access and exfiltrate proprietary data used in training LLMs, posing a severe risk to business confidentiality and competitive advantage.
Broadening the Attack Surface
Hosted LLM Models
All major cloud providers offer LLM services, including Azure Machine Learning, GCP’s Vertex AI, and AWS Bedrock.
These platforms let developers quickly access popular LLM-based AI models.
The screenshot below shows that the user interface is simple, allowing developers to build apps rapidly.
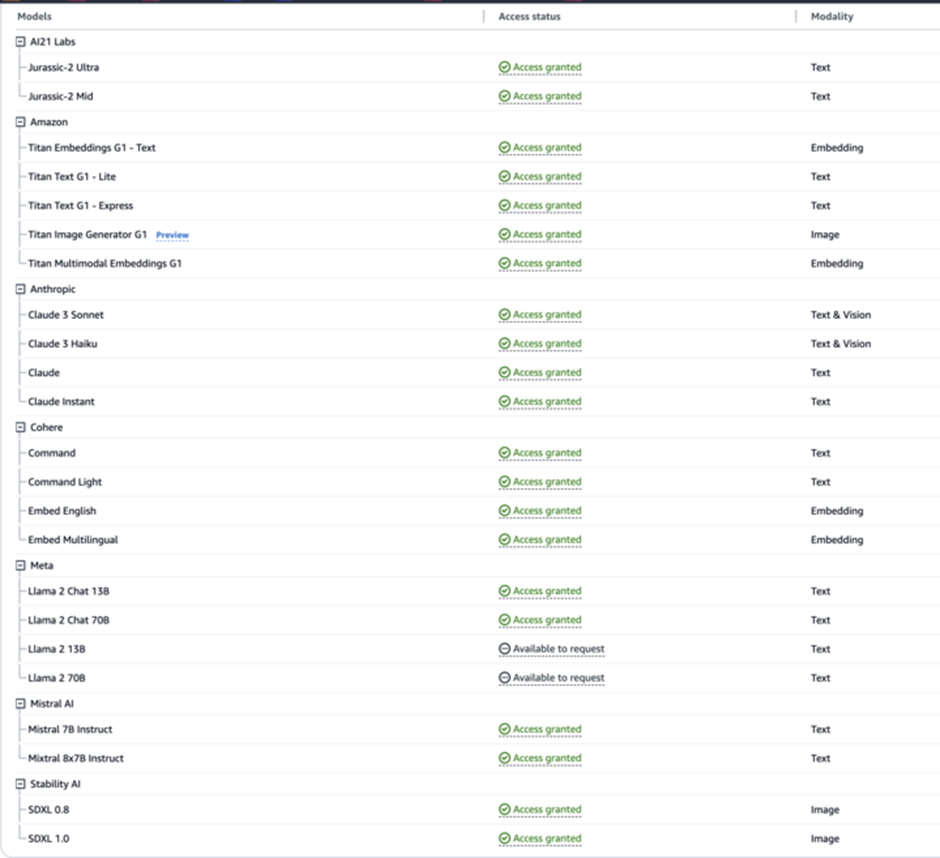
These models are disabled by default. To run them, the cloud vendor must be contacted.
Some models automatically approve, but third-party models require a brief form.
After a request, the cloud vendor usually grants access immediately.
The request requirement is generally a speed barrier for attackers, not a security measure.
LLM Reverse Proxy
A reverse proxy like this could help attackers make money if they collected proper passwords and wanted to sell access to the LLM models.
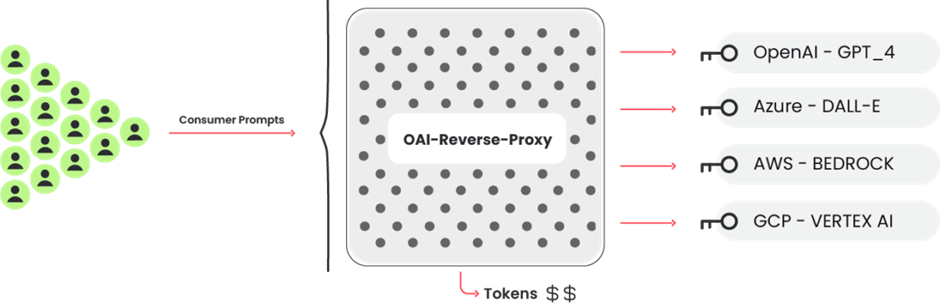
The Sysdig investigation revealed that the attack tools were configured to probe credentials across multiple AI platforms, indicating a systematic attempt to exploit any accessible LLM service.
This broad approach suggests that the attackers are not just seeking financial gain but also possibly aiming to harvest a wide range of data from various sources.
InvokeModel
Below is a malicious CloudTrail event from the InvokeModel call. A valid request was received with “max_tokens_to_sample” set to -1.
Although this faulty error creates the “ValidationException” error, it alerts the attacker that the credentials have access to the LLMs and are enabled.
They would have gotten “AccessDenied” otherwise.
{
"eventVersion": "1.09",
"userIdentity": {
"type": "IAMUser",
"principalId": "[REDACTED]",
"arn": "[REDACTED]",
"accountId": "[REDACTED]",
"accessKeyId": "[REDACTED]",
"userName": "[REDACTED]"
},
"eventTime": "[REDACTED]",
"eventSource": "bedrock.amazonaws.com",
"eventName": "InvokeModel",
"awsRegion": "us-east-1",
"sourceIPAddress": "83.7.139.184",
"userAgent": "Boto3/1.29.7 md/Botocore#1.32.7 ua/2.0 os/windows#10 md/arch#amd64 lang/python#3.12.1 md/pyimpl#CPython cfg/retry-mode#legacy Botocore/1.32.7",
"errorCode": "ValidationException",
"errorMessage": "max_tokens_to_sample: range: 1..1,000,000",
"requestParameters": {
"modelId": "anthropic.claude-v2"
},
"responseElements": null,
"requestID": "d4dced7e-25c8-4e8e-a893-38c61e888d91",
"eventID": "419e15ca-2097-4190-a233-678415ed9a4f",
"readOnly": true,
"eventType": "AwsApiCall",
"managementEvent": true,
"recipientAccountId": "[REDACTED]",
"eventCategory": "Management",
"tlsDetails": {
"tlsVersion": "TLSv1.3",
"cipherSuite": "TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256",
"clientProvidedHostHeader": "bedrock-runtime.us-east-1.amazonaws.com"
}
}GetModelInvocationLoggingConfiguration
Interestingly, the attackers were interested in the service configuration.
Calling “GetModelInvocationLoggingConfiguration” delivers S3 and Cloudwatch logging configuration if enabled.
Our solution utilizes S3 and Cloudwatch to collect as much attack data as feasible.
{
"logging config": {
"cloudWatchConfig": {
"logGroupName": "[REDACTED]",
"roleArn": "[REDACTED]",
"largeDataDeliveryS3Config": {
"bucketName": "[REDACTED]",
"keyPrefix": "[REDACTED]"
}
},
"s3Config": {
"bucketName": "[REDACTED]",
"keyPrefix": ""
},
"textDataDeliveryEnabled": true,
"imageDataDeliveryEnabled": true,
"embeddingDataDeliveryEnabled": true
}
}The victim pays more in LLMjacking attacks.
It should be no surprise that LLMs are expensive and can pile up rapidly.
A worst-case situation where an attacker utilizes Anthropic Claude 2.x and reaches the quota restriction in many locations might cost the victim over $46,000 per day.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
Given the sophistication and potential impact of LLMjacking, organizations are advised to adopt a multi-layered security strategy:
- Vulnerability Management: Regular updates and patches are crucial to defend against the exploitation of known vulnerabilities.
- Credential Management: Organizations must ensure that credentials are securely managed and not exposed to potential theft.
- Cloud Security Tools: Utilizing Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) can help minimize permissions and reduce the attack surface.
- Monitoring and Logging: Vigilantly monitoring cloud logs and enabling detailed logging of LLM usage can help detect suspicious activities early.
The emergence of LLMjacking highlights a growing trend of cyberattacks targeting advanced technological frameworks.
As organizations increasingly rely on AI and cloud services, the imperative to fortify cybersecurity measures has never been more urgent.
By understanding the tactics employed by attackers and implementing robust security protocols, businesses can safeguard their digital assets against these evolving threats.
Is Your Network Under Attack? - Read CISO’s Guide to Avoiding the Next Breach - Download Free Guide
%20(1)%20(1).webp?w=696&resize=696,0&ssl=1)


